Helm provides a quick way of setting up a Redis cluster using a pre-made Helm chart.
1. Add the Helm repository containing the Redis chart you wish to install.I will use for this tutorial bitnami repo.
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami2. Update local Helm repositories.
helm repo update3. Use helm install to install the chart. The basic command is as follows:
helm install my-release bitnami/redis4. Export the Redis password as an environment variable.
export REDIS_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace default redis-test -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 --decode)You can check it then with echo $REDIS_PASSWORD
That’s all, helm chart installed, but all pods are in Pending status?
In my case there was no Persistent volumes created so I needed to create it manually.
Create file pv.yaml and paste the content below:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: redis-data-redis-master0
spec:
capacity:
storage: 8Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: "/storage/data-master0"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: redis-data-redis-replicas0
spec:
capacity:
storage: 8Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: "/storage/data-replicas0"Now lets create persistent volume:
kubectl apply -f pv.yamlCreate and give necessary permissions to redis storage folder:
mkdir /storage
chown 10001:10001 /storage/Wait a bit and check if everything is working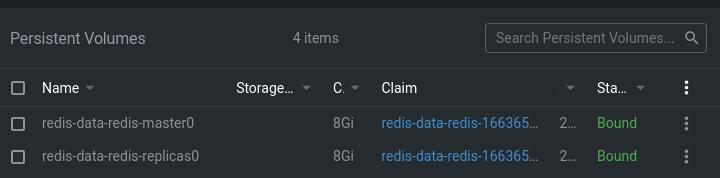
or with the command
kubectl get pv
**If you want to disable password authentication
helm upgrade redis-1669709819 bitnami/redis --set auth.enabled=falseAs a bonus let’s deploy Redis commander
redis commander is a redis web management tool written in node.js
Create redis-commander.yaml file and paste the content below:
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis-commander
annotations:
container.apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/redis-commander: runtime/default
container.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/redis-commander: runtime/default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis-commander
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis-commander
tier: backend
spec:
automountServiceAccountToken: false
containers:
- name: redis-commander
image: rediscommander/redis-commander
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: REDIS_HOST
value: "redis-1669709819-master"
- name: K8S_SIGTERM
value: "1"
ports:
- name: redis-commander
containerPort: 8081
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /favicon.png
port: 8081
initialDelaySeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
# adapt to your needs base on data stored inside redis (number of keys and size of biggest keys)
# or comment out for less secure installation
resources:
limits:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "512M"
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-commander
spec:
ports:
- port: 8081
targetPort: 8081
name: redis-commander
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: redis-commander
type: LoadBalancerNow create deployment
kubectl apply -f redis-commander.yamlNow you can access redis commander on port 8081
Option 2. Production Redis Statefulset NON-Bitnami cluster
Configuration:
3 Master nodes (redis-master-0, redis-master-1, redis-master-2)
3 Replica nodes (redis-replica-0, redis-replica-1, redis-replica-2)
Storage: 10Gi per pod using rook-cephfs
Resources: 512Mi-2Gi memory, 500m-1000m CPU per pod
Pod anti-affinity for high availability---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: redis-cluster-config
namespace: redis
data:
redis.conf: |
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes.conf
cluster-node-timeout 15000
cluster-require-full-coverage no
port 6379
bind 0.0.0.0
protected-mode no
tcp-keepalive 300
timeout 0
# Authentication (disabled)
# requirepass ""
# masterauth ""
maxmemory 3gb
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
appendonly yes
appendfsync everysec
loglevel notice
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes
rdbcompression yes
rdbchecksum yes
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: redis-master
namespace: redis
spec:
serviceName: redis-master
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis
role: master
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis
role: master
spec:
securityContext:
fsGroup: 999
runAsUser: 999
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:8.4-alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
name: redis
- containerPort: 16379
name: cluster
command:
- redis-server
- /etc/redis/redis.conf
- --cluster-announce-ip
- $(POD_IP)
- --cluster-announce-port
- "6379"
- --cluster-announce-bus-port
- "16379"
env:
- name: POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
volumeMounts:
- name: redis-data
mountPath: /data
- name: redis-config
mountPath: /etc/redis
resources:
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
limits:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "1000m"
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- redis-cli
- ping
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- redis-cli
- ping
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
volumes:
- name: redis-config
configMap:
name: redis-cluster-config
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: redis
role: master
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: redis-data
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
storageClassName: rook-cephfs
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: redis-replica
namespace: redis
spec:
serviceName: redis-replica
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis
role: replica
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis
role: replica
spec:
securityContext:
fsGroup: 999
runAsUser: 999
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:8.4-alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
name: redis
- containerPort: 16379
name: cluster
command:
- redis-server
- /etc/redis/redis.conf
- --cluster-announce-ip
- $(POD_IP)
- --cluster-announce-port
- "6379"
- --cluster-announce-bus-port
- "16379"
env:
- name: POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
volumeMounts:
- name: redis-data
mountPath: /data
- name: redis-config
mountPath: /etc/redis
resources:
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
limits:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "1000m"
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- redis-cli
- ping
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- redis-cli
- ping
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
volumes:
- name: redis-config
configMap:
name: redis-cluster-config
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: redis
role: replica
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: redis-data
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
storageClassName: rook-cephfs
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-master
namespace: redis
spec:
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: redis
role: master
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
name: redis
- port: 16379
targetPort: 16379
name: cluster
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-replica
namespace: redis
spec:
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: redis
role: replica
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
name: redis
- port: 16379
targetPort: 16379
name: cluster
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-cluster
namespace: redis
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: redis
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
name: redis
- port: 16379
targetPort: 16379
name: clusterAccess:
- Service: redis-cluster.redis.svc.cluster.local:6379
- Cluster port: 16379 (for cluster bus)
