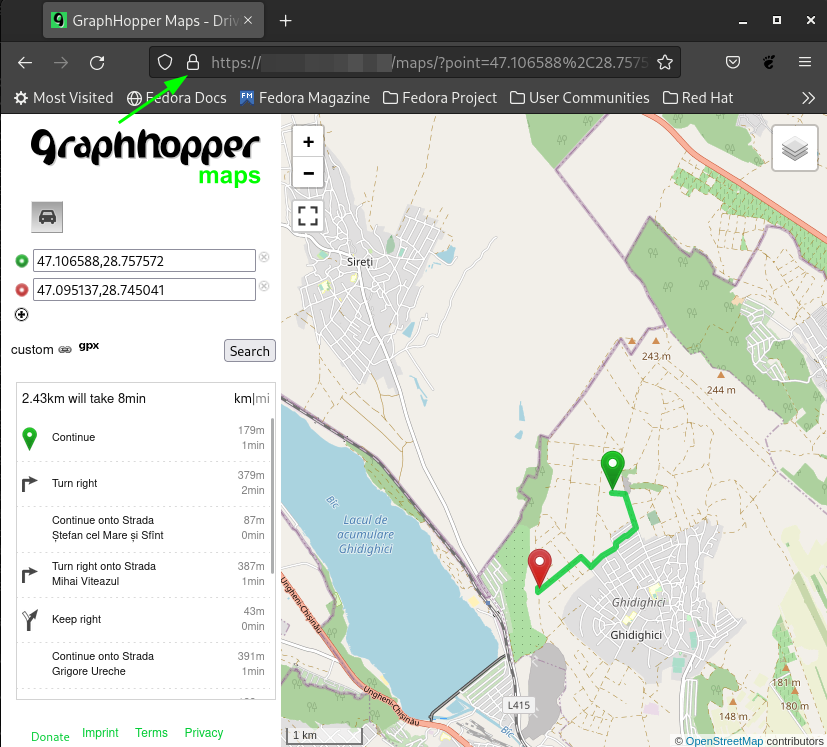
In this comprehensive ingress guide, you will learn how tosetup Nginx ingress controlleron Kubernetes and configure ingress using DNS.
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes cluster
- kubectl utility installed and authenticated to kubernetes cluster.
- Admin access to kubernetes cluster.
- A valid domain name to point to ingress controller Load Balancer IP.
- Helm 3 installed.First lets add a repository for NGINX to Helm:
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
Update the dataset to create an application instance in the Kubernetes cluster:
helm repo update
Result:
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories... ...Successfully got an update from the "ingress-nginx" chart repository Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈
Install the NGINX Ingress Controller
Install the controller in the standard configuration:
helm install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx
Create Kubernetes TLS secret
Let’s create a Kubernetes secret of type TLS with the
server.crtandserver.keyfiles (SSL certificates). We are creating the secret in the default namespace where we will have a graphhopper app deployment.
* Make sure that your deployment, ingress and secret are in the same namespace.Execute the following kubectl command from the directory where you have the
server.crtand key files or provide the absolute path of the files .kubectl create secret tls graph-tls-certificate --namespace default --key server.key --cert server.crt
Create the graph.yaml YAML file with the Ingress, Service, Deployment, HPA and volumes object manifests:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: graph labels: app: graph spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: graph template: metadata: labels: app: graph spec: containers: - name: graph image: israelhikingmap/graphhopper command: ["/bin/bash"] args: ["-c", "java -Ddw.graphhopper.datareader.file=/data/europe-latest.osm.pbf -Ddw.server.application_connectors[0].bind_host=0.0.0.0 -Ddw.server.application_connectors[0].port=8989 -jar *.jar server config-example.yml"] ports: - containerPort: 8989 volumeMounts: - name: graph mountPath: "/data/" volumes: - name: graph persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: graph --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: graph spec: selector: app: graph ports: - protocol: TCP port: 8989 targetPort: 8989 type: LoadBalancer #externalIPs: #- Your.external.ip #uncomment this only if you have local k8s cluster deployment --- apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: minimal-ingress annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx" spec: tls: - hosts: - <your domain URL> secretName: graph-tls-certificate rules: - host: <your domain URL> http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: graph port: number: 8989 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: graph spec: storageClassName: manual accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 1Gi --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: graph spec: storageClassName: manual capacity: storage: 1Gi accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce hostPath: path: /home/root2/graphhopper/data/ --- kind: StorageClass apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: manual provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer --- apiVersion: autoscaling/v2 kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler metadata: name: graph-memory-scale spec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: graph minReplicas: 1 maxReplicas: 6 metrics: - type: Resource resource: name: memory target: type: Utilization averageValue: 5Gi* At this moment, you already should have graphhopper data folder with .pbf map, in my case it’s located at /home/root2/graphhopper/data/
Create objects in a Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f graph.yaml
And in seconds you should have everything created, up and running, let’s check:
Find out the IP address of the Ingress controller (the value in the
EXTERNAL-IPcolumn):kubectl get svc
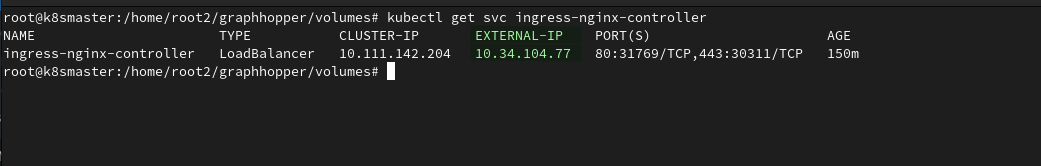
Host an A record with your DNS provider or on your own DNS server that will indicate the public IP address of the Ingress controller:
<your domain name > IN A <your external IP>
Test how TLS works
curl https://<your domain>